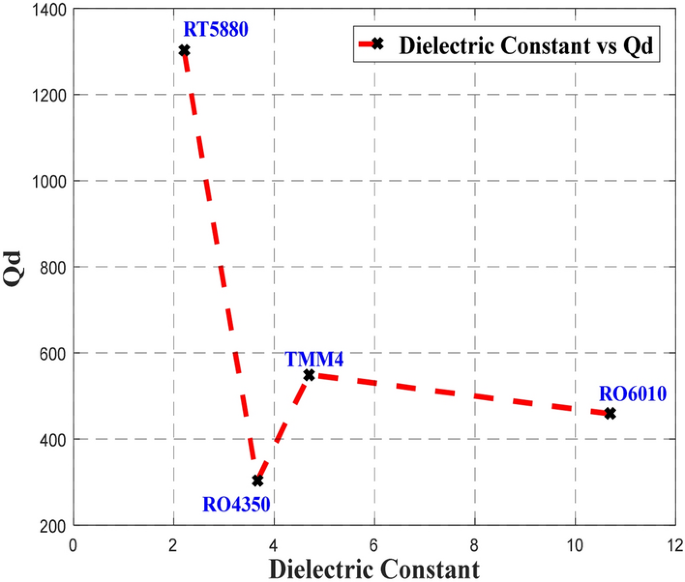
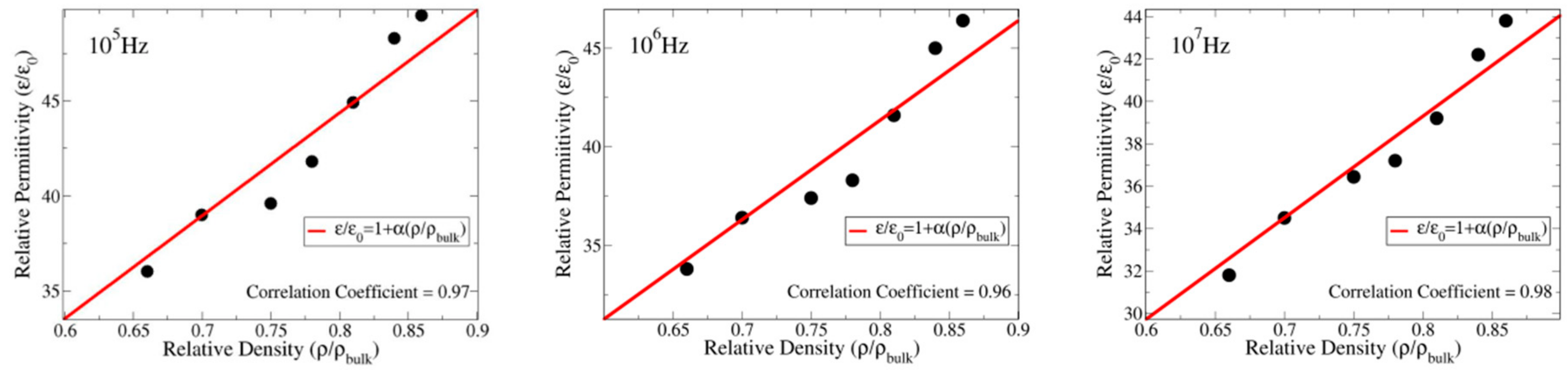
Ceramic Antenna Dielectric Constant

The antenna was fabricated on 1 mm thick al 2 o 3 ceramic material with relative dielectric constant of 9 8 relative permeability of 1 and ideal loss tangent of 0 when modeled without any conducting ground plane.
Ceramic antenna dielectric constant. A dielectric resonator antenna dra is a radio antenna mostly used at microwave frequencies and higher that consists of a block of ceramic material of various shapes the dielectric resonator mounted on a metal surface a ground plane radio waves are introduced into the inside of the resonator material from the transmitter circuit and bounce back and forth between the resonator walls. For gps applications high dielectric constant. It is a high performance antenna designed for embedded applications. Smaller physical size and wider bandwidth are two antenna engineering goals of great interest in the wireless world.
Antennas in use for mimo applica tions. The dielectric constant of most silicon nitride materials is greater than 7. To this end the concept of external substrate perforation is applied to patch antennas in this paper. Silicon nitride is a material that is commonly used in missile radome and antenna applications due to its dielectric properties temperature capability and strength toughness.
At present microwave ceramic powder dielectric constant 10 120 have mature products can be applied to dielectric antennas dielectric resonators dielectric filters etc dielectric antenna direction gps beidou positioning system required frequency bands have products production and sales devices required for base station systems are being developed in an orderly manner these products. As previously stated mimo tech nology will demand multiple individual antenna elements in closely spaced base stations. There will certainly be a demand for inexpensive antennas and for low dielectric constants to improve the efficiency and bandwidth. A dielectric antenna is composed of ceramic patch and pin.
It is used primarily to provide proper spacing and mechanical support between the patch and its ground plane. The goal was to overcome the undesirable features of thick and high dielectric constant substrates for patch antennas without sacrificing any of the desired features. The use of the al 2 o 3 ceramic material substrate and its high dielectric constant made it possible to shrink the dimensions of the patch antenna. Although it is suitable for many applications a lower dielectric constant is often preferred.
This embedded patch antenna is made by designing an antenna on a medium with high dielectric constant such as ceramic ceramic is a kind of common mediums to make antennas. The substrate generally has a thickness in the range of 0 01 0 05 free space wavelength λ0. Figure 1 shows examples of different radiating structures that can be used for dielectric resonator antennas.