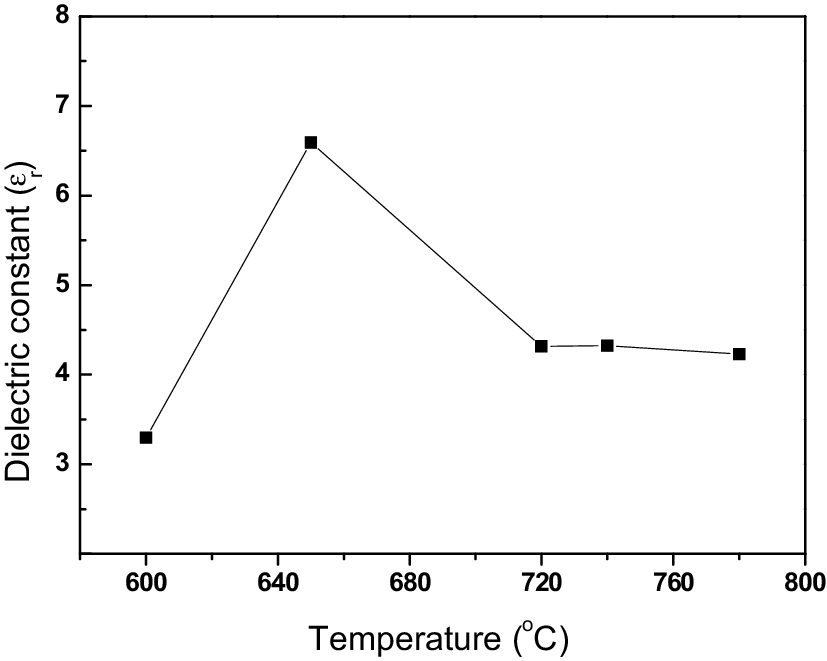
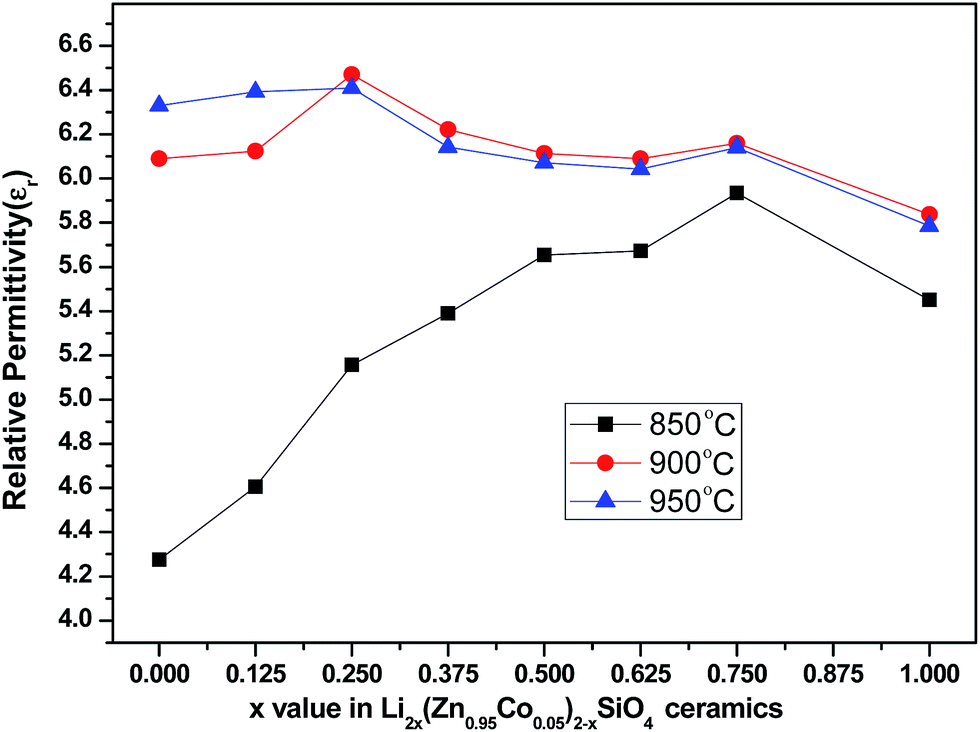
Glass Ceramic Dielectric Constant
The relative permittivity or dielectric constant of a material is its absolute permittivity expressed as a ratio relative to the vacuum permittivity.
Glass ceramic dielectric constant. The dielectric constant is the relative permittivity of a material compared to a vacuum or free space. Relative permittivity is the factor by which the electric field between the charges is decreased relative to vacuum. In this work the dielectric spectrum testing combined with other analytical methods such as 7li solid state nuclear magnetic resonance x ray photoelectron spectroscopy and the electrochemical method have been applied to investigate the dual doping behaviors of ws2 and libr within li7p3s11 glass ceramic electrolytes. The coefficient of thermal expansion cte of l glass fiber is 3 9 ppm c compared to 5 4 ppm c for e glass.
Baal 2 si 2 o 8 li 2 o mgo zno b 2 o 3 sio 2 bas lmzbs glass ceramics were prepared through the solid state route. The phase transformation microstructure bulk density and microwave dielectric properties of 1 x baal 2 si 2 o 8 xlmzbs x 0 1 0 4 the glass ceramics were examined the effects of the lmzbs additive as a mineralizer on the hexagonal to monoclinic transformation. Glass ceramics are polycrystalline materials produced through controlled crystallization of base glass. Ptfe based systems to use a higher glass loading.
Dielectric strength is the maximum voltage field that the ceramic or material can withstand before electrical breakdown occurs. Glass ceramic materials share many properties with both glasses and ceramics glass ceramics have an amorphous phase and one or more crystalline phases and are produced by a so called controlled crystallization in contrast to a spontaneous crystallization which is usually not wanted in. Dielectric constant k is a number relating the ability of a material to carry alternating current to the ability of vacuum to carry alternating current the capacitance created by the presence of the material is directly related to the dielectric constant of the material. Where k is the real dielectric constant and c and c 0 are capacitance with and without the dielectric respectively.
Permittivity is a material property that affects the coulomb force between two point charges in the material.