Cap Floor Collar Finance
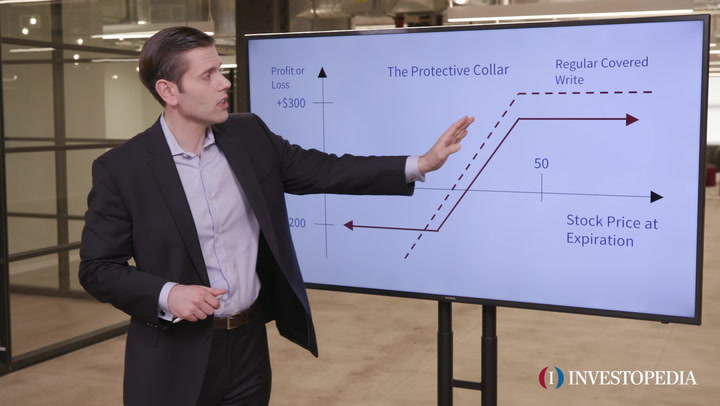

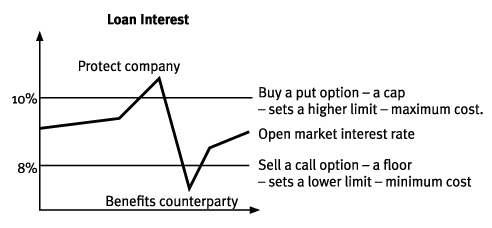
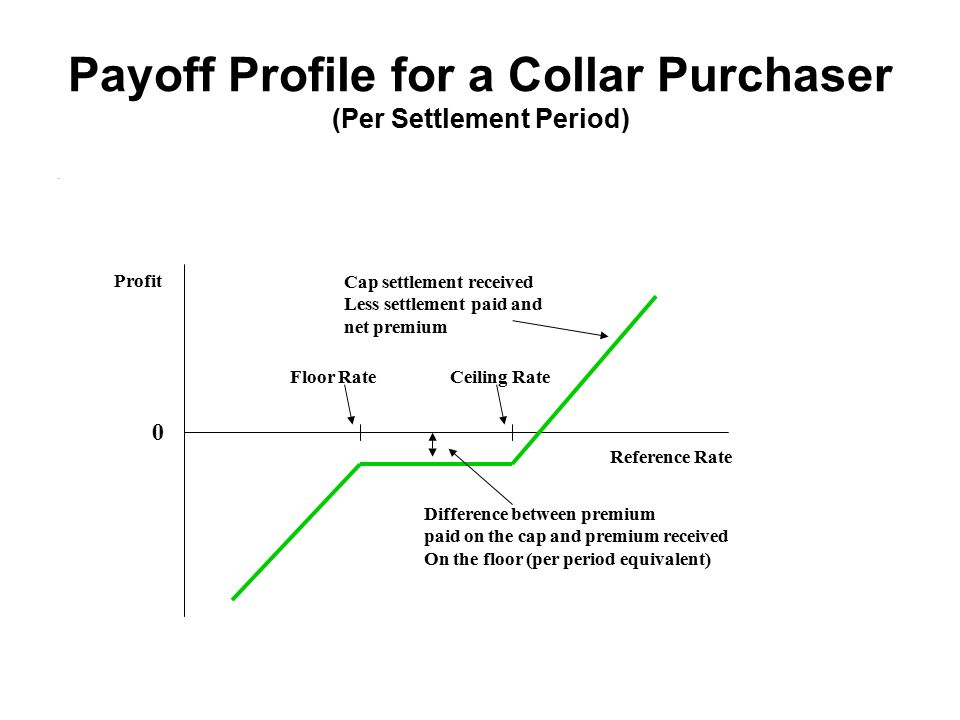
An interest rate collar can be created by buying a cap and selling a floor.
Cap floor collar finance. It is a type of positive carry collar that is constructed by simultaneously purchasing and selling of out of the money calls and puts with the strike prices of which creating a band encircled by an upper and lower bound. Cap and floor payoffs and interest rate collars. Collar break even point bep and profit loss p l an investor s break even point on this strategy is the net of the premiums paid and received for the put and call subtracted from or added to. An option based strategy that is designed to establish a costless position and secure a return.
The premium for an interest rate collar also depends on the rollover frequency and how you make your premium payments. Un floor est un contrat de taux d intérêt qui moyennant le paiement d une prime permet à son acheteur de se couvrir ou de tirer profit d une baisse des taux monétaires en deçà d un certain niveau. We assume that interest rate rises 5 each quarter in 2 years starting from 2. For example as a borrower with current market rates at 6 you would pay more for an interest rate collar with a 4 floor and a 7 cap than a collar with a 5 floor and a 8 5 cap.
A company would like to buy cap at 4 for hedging purposes costing 100 000. This organization has purchased a 5 cap and sold a 2 floor which provides the organization with an interest rate collar of 2 to 5. The enhancement consists of additions which increase the cost of the floor should it be breached or other adjustments designed to increase its cost. Interest rate swap in hedging variable rate debt with a swap an organization agrees to pay out a fixed amount each month to a counterparty in exchange for receipt of a variable rate payment that approximates the organization s debt.
Given the 50 million loan over 2 years period we can make speculation how cap floor and collar would make a difference. An interest rate cap is a derivative in which the buyer receives payments at the end of each period in which the interest rate exceeds the agreed strike price an example of a cap would be an agreement to receive a payment for each month the libor rate exceeds 2 5. A collar involves selling a covered call and simultaneously buying a protective put with the same expiration establishing a floor and a cap on interest rates. They are most frequently taken out for periods of between 2 and 5 years although this can vary considerably.
While the collar effectively hedges. A structured collar describes an interest rate derivative product consisting of a straightforward cap and an enhanced floor.


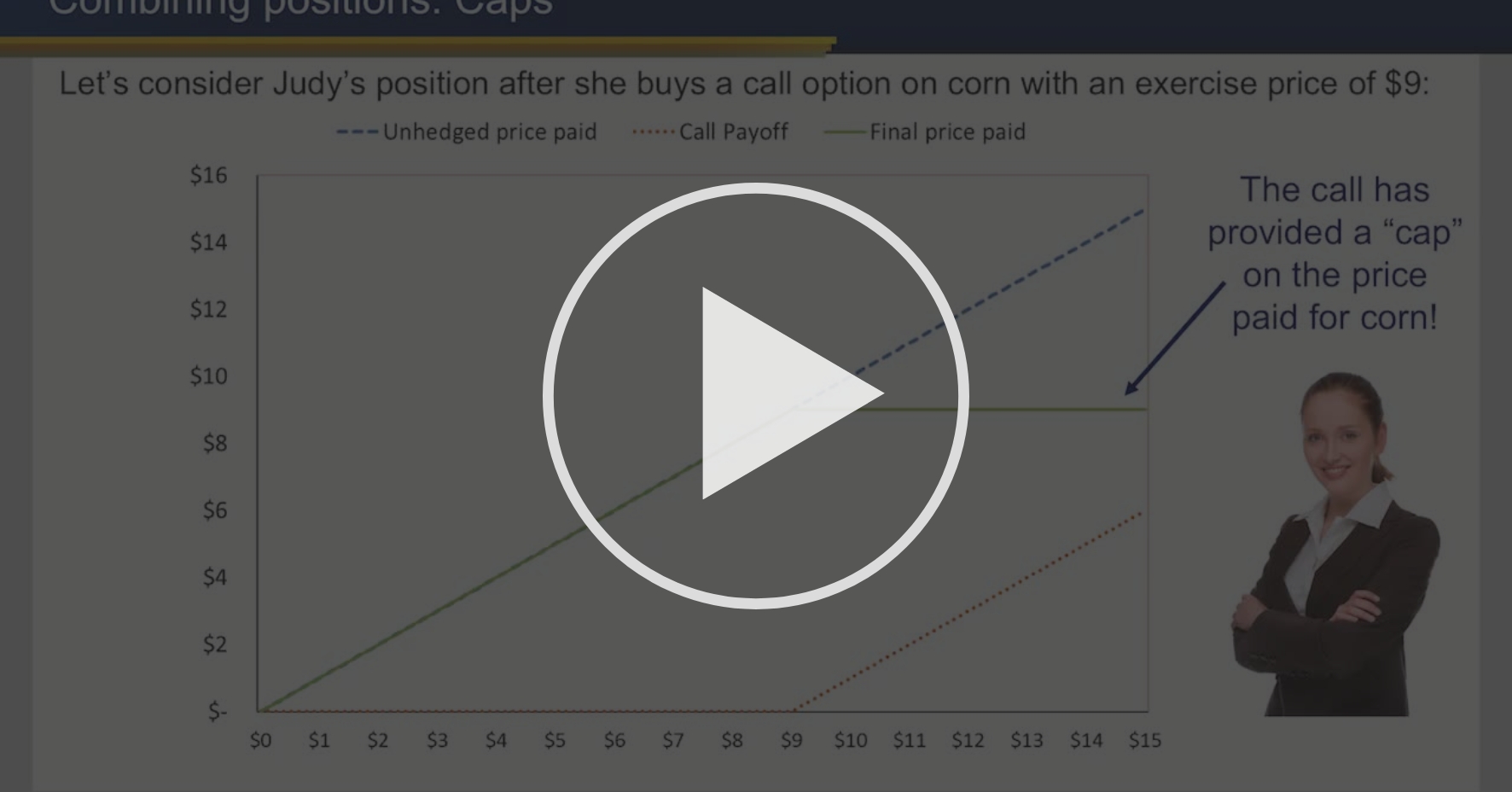
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/strategy-4086857_19201-23485cf7c4bf4dbbb95c93f267285f16.jpg)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Zero_Cost_Collar_Apr_2020-01-3f7ffff9ccd84d9e8f93fa3cd72c8d4f.jpg)
/10OptionsStrategiesToKnow-02_2-8c2ed26c672f48daaea4185edd149332.png)