Carbon Dioxide Hydrate On Ocean Floor

The study was conducted near norway s svalbard islands above several seafloor methane.
Carbon dioxide hydrate on ocean floor. But this approach also involves ecological risk. Furthermore aerobic oxidation of methane consumes oxygen. Ocean storage of carbon dioxide co 2 is a method of carbon sequestration the concept of storing carbon dioxide in the ocean was first proposed by italian physicist cesare marchetti in his 1976 paper on geoengineering and the carbon dioxide problem since then the concept of sequestering atmospheric carbon dioxide in the world s oceans has been investigated by scientists engineers and. Carbon dioxide contributes to ocean acidification.
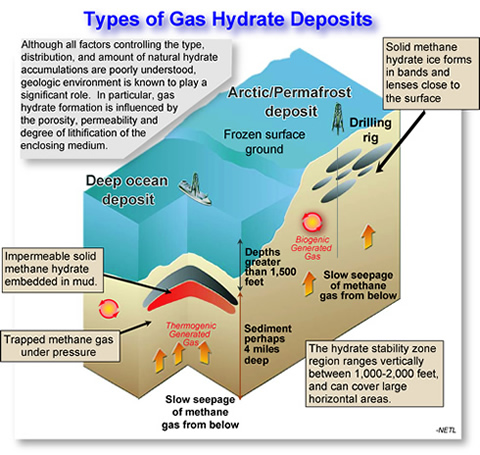
Bernhard and colleagues injected carbon dioxide hydrate directly into cylinders pushed into the deep sea floor sediment and incubated them in place for a month to learn whether benthic single celled organisms called foraminifera could survive the high co 2 high acidity method of carbon capture and sequestration known as direct injection of co. The oceanic carbon cycle or marine carbon cycle is composed of processes that exchange carbon between various pools within the ocean as well as between the atmosphere earth interior and the seafloor the carbon cycle is a result of many interacting forces across multiple time and space scales that circulates carbon around the planet ensuring that carbon is available globally. If instead carbon dioxide is stored as a hydrate within the cold deep sea floor it would be much safer because co 2 hydrates are considerably more thermally stable than methane hydrates. Once beneath the sea floor the carbon dioxide would interact with the surrounding fluids and produce hydrate ice crystals which would plug the rock pores serving as a secondary cap on the.
Massive amounts of carbon dioxide released from the deep ocean brought an end to the last ice age according to new research. In this process carbon dioxide is produced which dissolves in the water. Even warming of the sea floor would not destabilize them. In this paper storage of co 2 beneath the ocean floor is studied while storage in depleted gas reservoirs is studied in the companion paper.
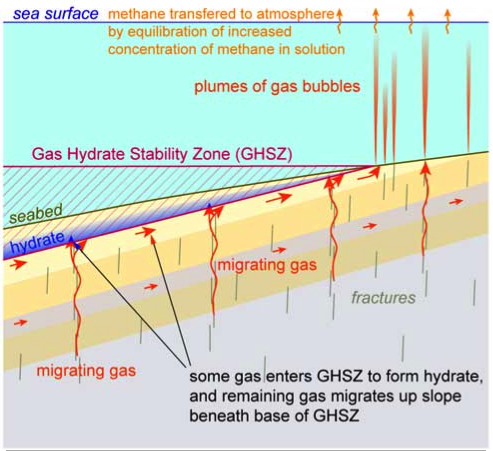
The ocean waters near the surface of the arctic ocean absorbed 2 000 times more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere than the amount of methane that escaped into the atmosphere from the same waters according to a study by the usgs gas hydrates project and collaborators in germany and norway. If those caps melt the carbon could seep into the ocean and ultimately into the. Hydrothermal vents like this one can have reservoirs of liquid co2 nearby kept in place by icy hydrate caps.