Floor And Ceiling Effects Definition

Although the traditional definition of.
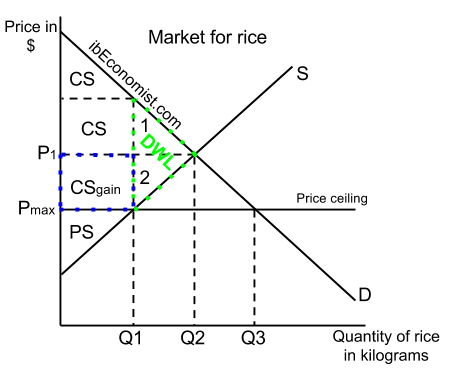
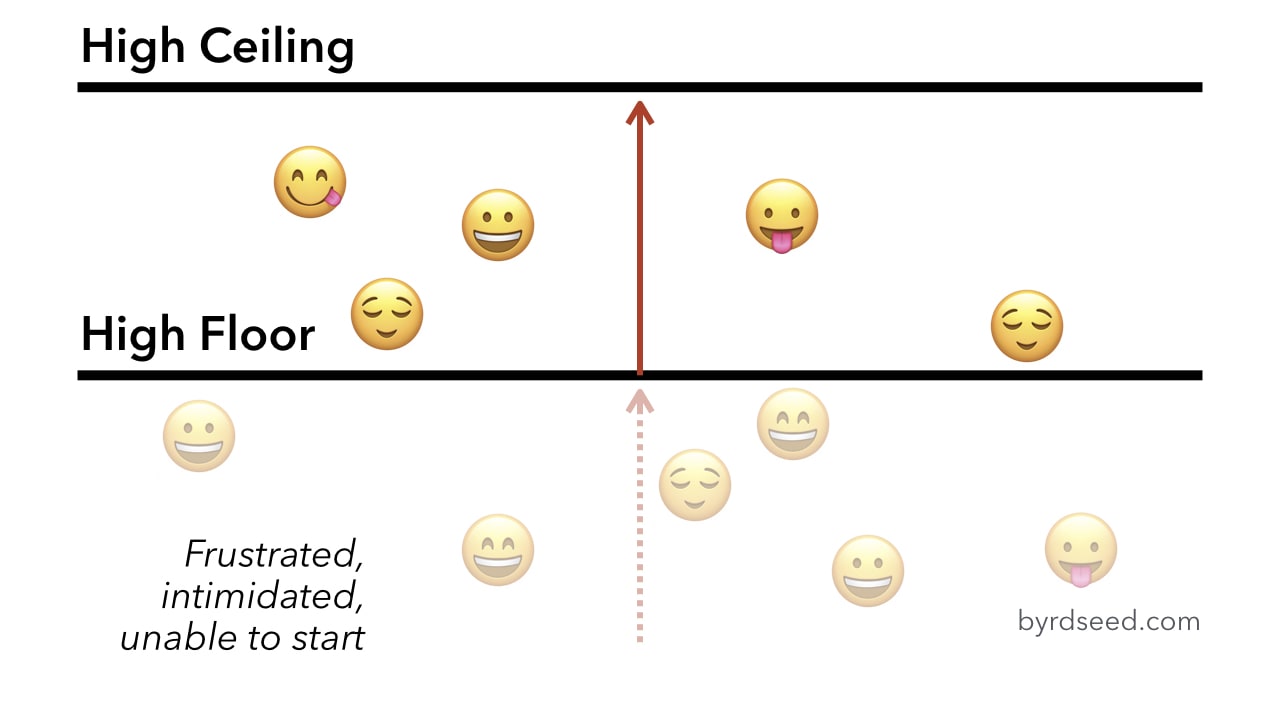
Floor and ceiling effects definition. The ceiling effect is said to occur when participants scores cluster toward the high end or best possible score of the measure instrument. A floor effect is when most of your subjects score near the bottom. The opposite is the floor effect. Floor and ceiling effects were considered present if 15 of patients achieved the worst score floor effect 0 48 or best ceiling effect 48 48 score.
This is even more of a problem with multiple choice tests. Psychology definition of floor effect. In statistics a floor effect also known as a basement effect arises when a data gathering instrument has a lower limit to the data values it can reliably specify. In pharmacology a ceiling effect is the point at which an independent variable which is the variable being manipulated is no longer affecting the dependent variable which is the variable being measured.
Some say int 3 65 4 the same as the floor function. It essentially describes when the dependent variable has leveled. This could be hiding a possible effect of the independent variable the variable being manipulated. Ceiling effects and floor effects both limit the range of data reported by the instrument reducing variability in the gathered data.
Thus the test score will not increase for a subsample of people who may have clinically improved because they have already reached the highest score that can be achieved on that test. Ceiling effect is used to describe a situation that occurs in both pharmacological and statistical research. A ceiling effect occurs when test items aren t challenging enough for a group of individuals. There is very little variance because the floor of your test is too high.
The inability of a test to measure or discriminate below a certain point usually because its items are too difficult. And this is the ceiling function. Let s talk about floor and ceiling effects for a minute. Limited variability in the data gathered on one variable may reduce the power of statistics on correlations between that variable and another variable.
In research a floor effect aka basement effect is when measurements of the dependent variable the variable exposed to the independent variable and then measured result in very low scores on the measurement scale. The int function short for integer is like the floor function but some calculators and computer programs show different results when given negative numbers. In some fields biology.