Causes Of Maternal Morbidity In India

What is india s maternal mortality ratio.
Causes of maternal morbidity in india. Can racial disparities in maternal deaths be reduced. Total annual deaths declined from 32 000 maternal deaths in 2015 to 30 000 deaths in 2017. While india s maternal mortality rate declined substantially during 2004 2006 to 2014 2016 at an annual rate of 5 the reduction is still short of what is required to achieve the national health policy target. Black american indian and alaska native ai an women are two to three times more likely to die from pregnancy related causes than white women and this disparity increases with age researchers from the centers for disease control and prevention cdc report today in the morbidity and mortality weekly report mmwr.
Between 2000 and 2017 the maternal mortality ratio mmr number of maternal deaths per 100 000 live births dropped by about 38 worldwide. The global lifetime risk of maternal death nearly halved between 2000 and 2017 from 1 in 100 to 1 in 190. We present the distribution of india s 2001 2003 maternal mortality by cause and uptake of emergency obstetric care in poorer and richer states. In india the ratio for maternal mortality rate to live births has fallen and by 2015 india plans to reduce its mmr to 109.
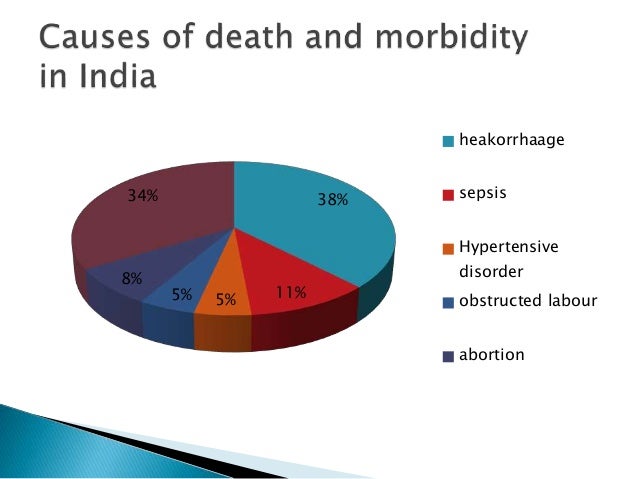
Shots health news black and native american women die of pregnancy related causes at a higher rate than white women. Jithin jose proposes a four pronged strategy to sustain and accelerate the decline raft review of medical records death certificates or autopsy reports of mothers. Methods and findings the registrar general of india surveyed all deaths occurring in 2001 2003 in. Haemorrhaging is the number one cause of maternal deaths 2.
Researchers say the. India lost the lives of 882 000 children under five and 143 000 children between the ages of five and fifteen in 2018. Every day in 2017 approximately 810 women died from preventable causes related to pregnancy and childbirth. Background data on cause specific mortality skilled birth attendance and emergency obstetric care access are essential to plan maternity services.
As per the sample registration system india s maternal mortality ratio has declined from 130 per 1 lakh live births in 2014 16 to 122 per 1 lakh live births in 2015 17. Most children under five die due to preventable or treatable causes such as complications during birth pneumonia diarrhoea neonatal sepsis and malaria unicef notes.




.jpg)